Biotechnology
China has significantly bolstered its biotechnology sector, prioritizing it in three of the seven cutting-edge science and technology fields in its 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025): brain science, genetic engineering, and clinical medicine. Biotech is also crucial to global development goals, particularly in public health, sustainable energy, and food security.
With sizeable domestic support, Chinese companies such as BGI (genome research), Beigene (anti-cancer drugs), Mindray (medical equipment) and WuXi Apptec (services and equipment for drug development) have risen to global prominence.
ChemChina took over Syngenta, the world’s third largest seed producer, in 2017. China is the world’s largest exporter of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs).
International collaboration and competition in biotech are intricately intertwined. China participates in roughly a third of the world’s multiregional clinical trials – only the US participates in more. China has also welcomed large investments by multinational pharmaceutical companies in domestic startups. At the same time, fair competition and market access remain a problem for many foreign firms in the healthcare sector, as localization efforts give domestic firms preferential treatment.
Great power competition adds further complexity. China, the US, and Europe all scrutinize the sharing of sensitive genetic and medical data. They also race for supremacy in dual-use technologies, such as brain-computer interfaces, which could be used for military robots.
Graphics dashboard
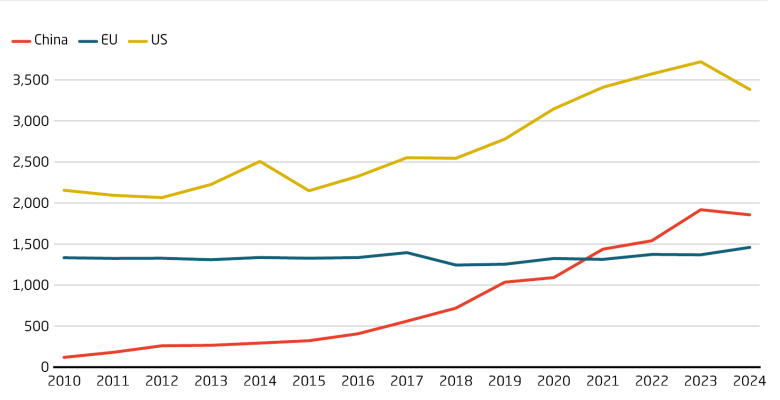
While the US is still the unchallenged leader, China has rapidly increased its number of invention patents over the last 20 years. It overtook the EU in 2021. China’s rise in global patent applications is consistent with increased interest from overseas investors in its biotech startups. In pharma, Chinese firms are getting increasingly successful in discovering me-too, me-better and more recently first-in-class drugs.
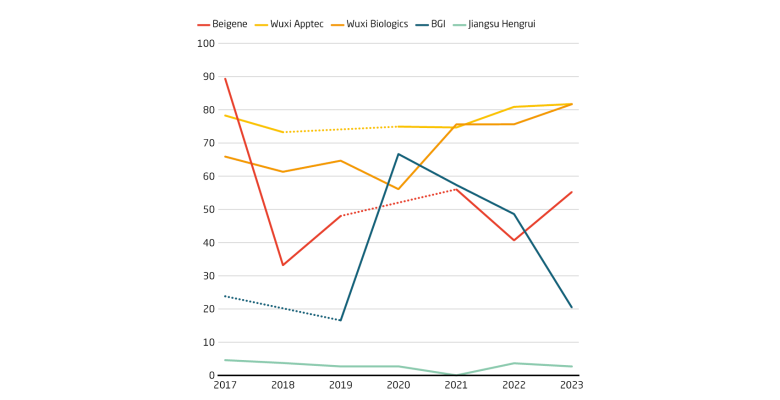
Several major Chinese biotech companies rely on the overseas market for their revenue, sometimes for over 80 percent. The decline of BGI’s overseas revenue share is likely associated with its addition to the US “entity list” in 2020. Only Jiangsu Hengrui generates almost all its revenue on the Chinese market. The company has partnerships with Merck and other foreign firms to jointly develop drugs, but does not directly export to overseas clients.
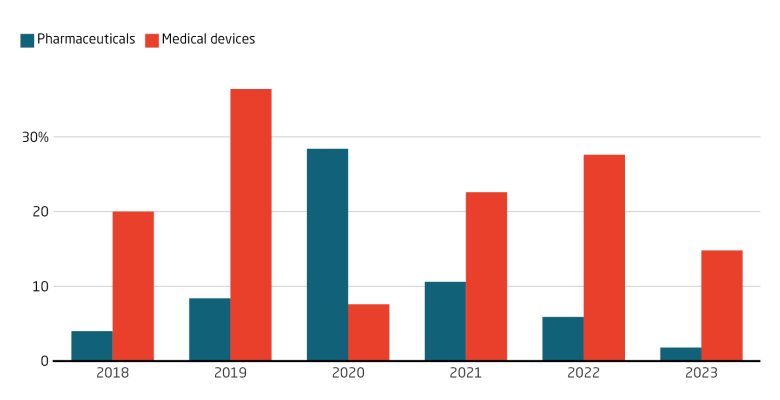
Investment has been pouring into China’s medical device sector, averaging 22 percent in annual growth between 2018 and 2023. The pharmaceutical sector has averaged 10 percent annual growth, with a significant spike at the start of the Corona pandemic. The government’s backing of biotech sectors has channeled both private and public capital into these industries.
Biotechnology in China: Timeline of crucial events
China approves its first COVID-19 vaccine for general public use, developed by state-backed pharmaceutical giant Sinopharm and the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine was approved for use in the EU.
Chinese medical device company Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics acquires Finnish biotech company HyTest Invest and its subsidiaries for EUR 532 million.
Leading Chinese medical imaging firm United Imaging invests EUR 410 million in a new manufacturing and research facility in Shanghai to rely heavily on automatic and intelligent processes.
The National Development and Reform Commission releases the 14th Five-Year Plan for the bioeconomy, covering life sciences and biotechnologies and calling for more investment in basic research.
MIIT calls for companies to participate in a new biomedical materials innovation program to increase collaborative innovation with a focus on polymer, metal and inorganic non-metallic materials.
MOST issues clarifying rules on human genetic resources, preventing foreign entities from collecting resources in China and restricting their access to them.
AstraZeneca acquired Gracell Biotechnologies for USD 1.2 billion, marking the first time a multinational drugmaker fully acquires a Chinese biotech firm.
The National Healthcare Security Administration aims to enhance coordination between local governments on centralized or volume-based procurement (high volume, low cost purchase of pharmaceuticals).


MIIT issues procurement guidelines, placing restrictions on a wide range of medical equipment, also X-ray machines, MRI & surgical equipment. The rules require 25, 50, 75 or 100 percent local content.
MIIT releases Five-Year Plans for the medical equipment & pharma industries, to ensure basic supplies & improve the industrial chain, enhance pharma innovation, modernization, & supply security 2025.
Chinese healthcare companies such as Andon Health and Beijing Hotgen Biotech see revenue surge thanks primarily to overseas sales of COVID-19 home testing kits.
Fosun Pharma and Genuine Biotech win the right to market the first China-made oral Covid-19 drug. The EU approved the first oral COVID-19 antiviral treatment, Pfizer’s drug Paxlovid, in January 2022.
MIIT releases a three-year plan to develop China’s non-food bio-based materials industry. By 2025, it aims for strong innovation capabilities to broaden its circular economy & reduce carbon emission.
Neusoft Medical launches China's first dual-energy 3.0T magnetic resonance imaging system. Chinese firms can make systems between 1.5T to 3.0T (magnetic field strengths) using only domestic inputs.
Caixin reports: China's outbound deals involving treatment rights exceeded inbound deals for the first time in 2023. Other parties can use a company’s products, technology or intellectual property.
- The Chinese Academy of Sciences has reported major progress in brain-computer interface (BCI) clinical trials. The test enabled a patient paralyzed by a spinal cord injury to advance from two-dimensional cursor control to interaction with the 3D physical world through an embodied intelligence robot. (Source (CN): STDaily, December 17, 2025)
- The first iteration of China’s Private Health Insurance Innovative Drug Catalogue includes 19 novel drugs. This tiered list prioritizes innovative drugs with “high levels of innovation and coverage exceeding the scope of basic medical insurance,” meaning they are recommended for commercial/private healthcare and do not enjoy guaranteed coverage. (Source (EN): fiercepharma, December 8, 2025)
- The Bayer E-Town Open Innovation Center opened in Beijing’s E-Town BioPark and aims to integrate industry, education, research, and entrepreneurship to strengthen China's innovation chain and integration into global markets, as well as to promote digitalization in healthcare. It is the first of its kind in China. (Source (EN/CN): Bayer, STDaily, November 15, 2025)
- The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) and the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) announced the first batch of 43 companies drafted to build biomanufacturing pilot capacity platforms. These scale-up facilities will pool resources, funding, and talent to increase strength in several biomanufacturing domains, from industrial applications to bioenergy and biopharma. (Source (CN): MIIT, November 10, 2025)
Publications



