
Artificial Intelligence
The Chinese government has long elevated artificial intelligence (AI) development to a strategic national priority with policies like the New-Generation AI Development Plan in 2017. It sees the potential of AI to radically transform social and productive structures due to its ability to perform tasks that usually require human intelligence.
US-China competition for dominance over AI technologies shapes today’s geopolitics. Wary of China’s potential, especially Beijing’s ambition to leverage AI for modernizing its military, the US has imposed sweeping export controls aimed at hobbling its progress.
Thanks to government support and global links, Chinese applied AI companies like computer vision firms SenseTime and Megvii are now household names. China’s fast-growing talent base and vibrant ecosystem of companies and public research labs are leading AI application development and producing high-impact AI research.
But China’s main weakness lies in its historical links with US industry: it trails in the fundamentals. China still cannot match the quality of US-designed AI chips and relies on machine learning frameworks developed by US firms. While China’s AI future is for now tied to choices made in Washington, in the long run, Chinese large language models and other types of AI systems may well prove good enough for the tasks they need to fulfill: enabling industrial applications and boosting military and security capabilities.
Graphics dashboard
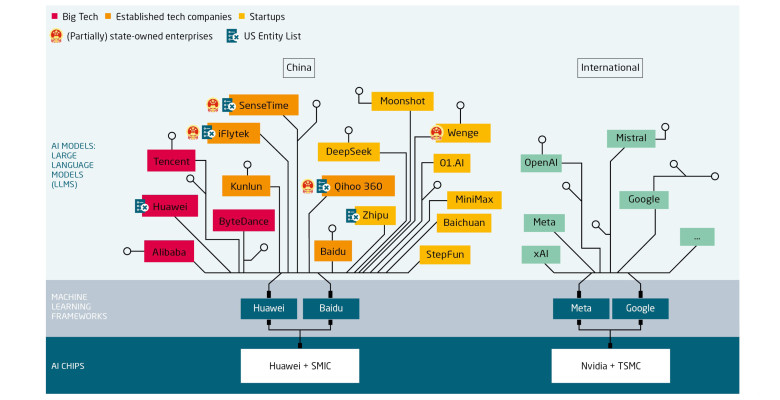
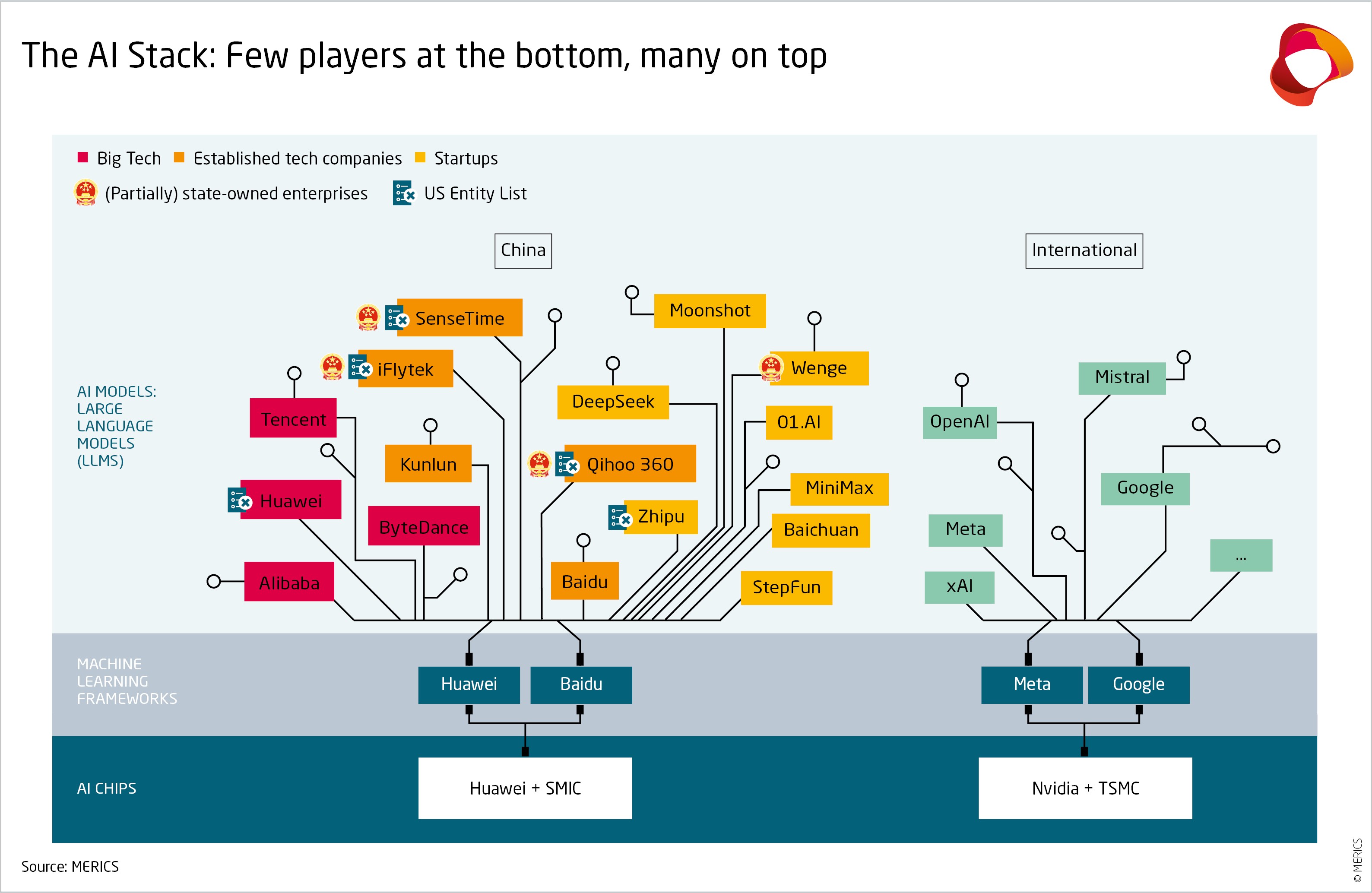
China is pursuing self-reliance in AI at every level of the technology. The government does this with a mixture of strategies, from heavy financial support for big players in semiconductors to policies enabling an active and open field in software. To learn more, read our report: “China’s drive toward self-reliance in artificial intelligence: from chips to large language models” here.
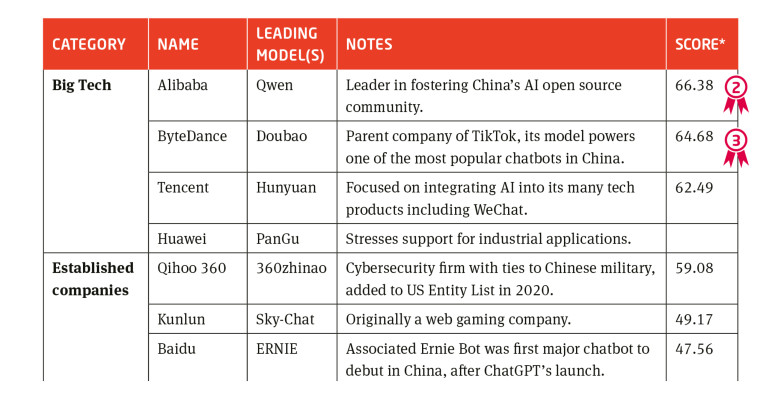
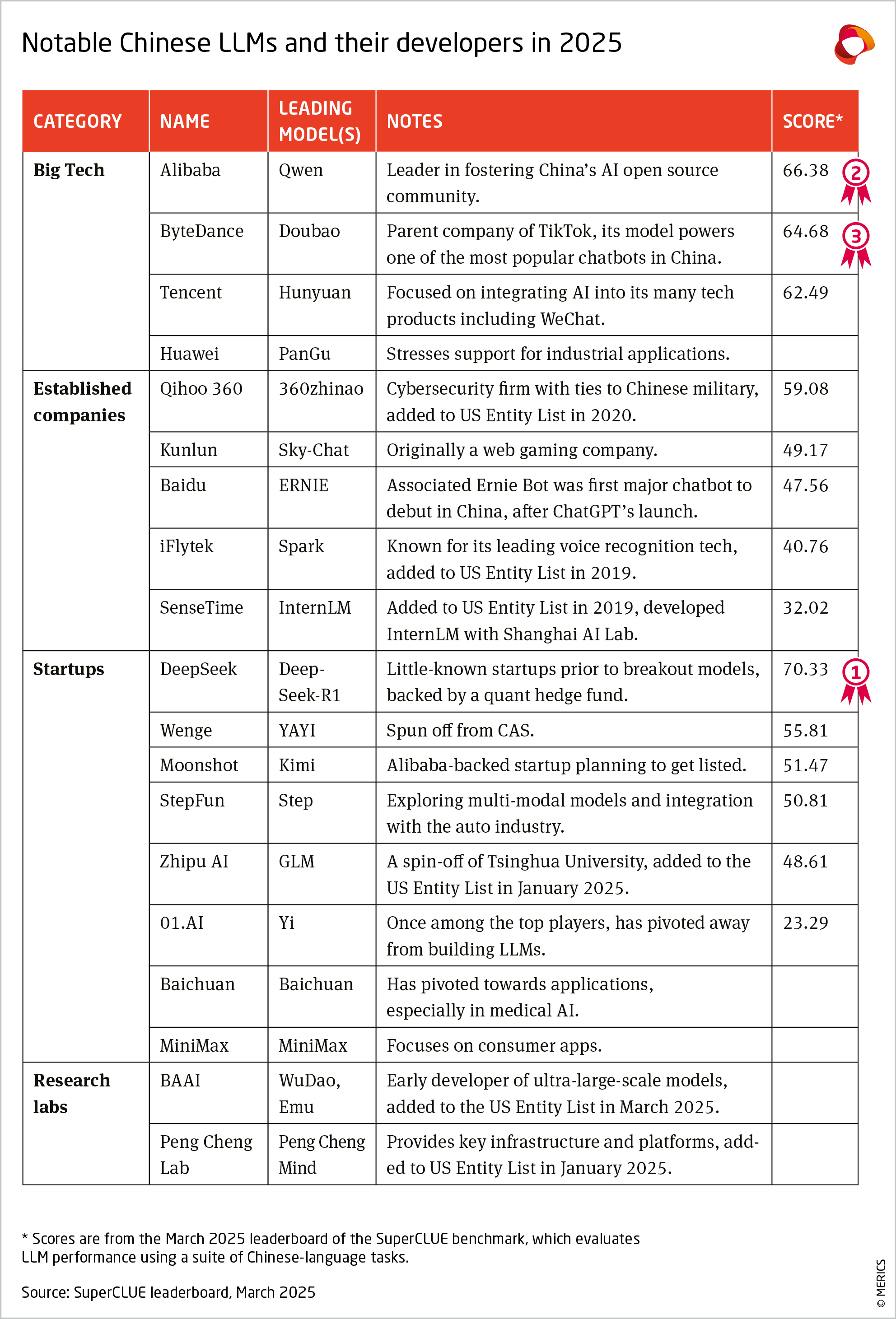
China’s LLM landscape includes a large number of players across Big Tech, established companies, startups, and research labs. The leading performers in March 2025 are DeepSeek, followed by tech giant Alibaba’s Qwen and TikTok parent company ByteDance’s Doubao.
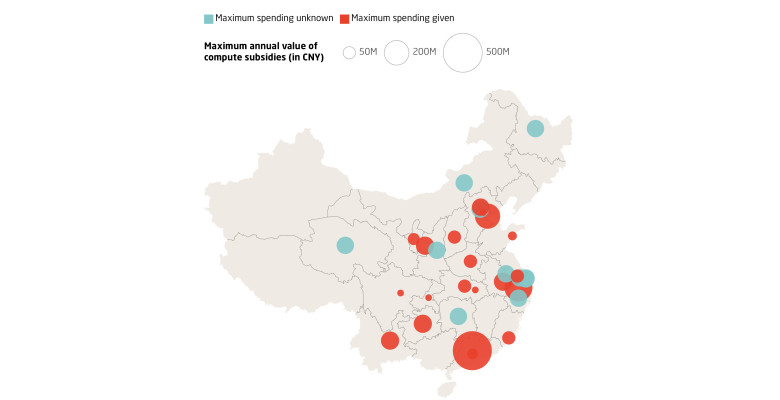
Although most primarily rely on private funding, LLM developers in China benefit from a supportive ecosystem which incentivizes model training and adoption. For example, several local governments have been issuing “compute vouchers” (算力券). A single organization can receive compute subsidies ranging from CNY 1 to 10 million per year, depending on the location, covering an average of 10-30 percent of expenses on a single purchase. Some subsidies are not available exclusively to LLM or AI developers.
Artificial Intelligence in China: Timeline of crucial events
Huawei releases deep learning software framework Mindspore to the open-source community, as China attempts to reduce reliance on Google and Meta frameworks.
China's algorithm filing portal goes online for recommender engines, the genesis of a licensing system later used for generative AI and large language models (LLMs).
China releases rules on synthetic (AI-generated) content, motivated by concerns around deepfakes.
Tsinghua University's Knowledge Engineering Group announces the bilingual pre-trained model ChatGLM-130B and its open-source version, ChatGLM-6B. The team founds Zhipu AI.
Baichuan-Inc, a startup of the founder of internet search engine Sugou, releases its first open-source LLM. The Baichuan series is among the best performing in China.
Chinese AI experts led by a team at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS) publish recommendations for a comprehensive AI law after legislation is added to the State Council's work plan.
China restricts access to Hugging Face, the top international platform for open-source AI collaboration. China’s open-source community is displeased but seeks alternatives to work on leading models.
Yi-34B, a model from leading startup 01.AI, tops the international leaderboard for open-source LLMs. But it becomes mired in controversy over the way it referenced Meta's Llama2 architecture.
Chinese online retailer Alibaba announces investment in LLM startup MiniMax, following similar investments in Zhipu AI, Baichuan AI, 01.AI, and Moonshot AI.
Tsinghua and ShengShu Technology unveil Vidu, a text-to-video generator and China's answer to OpenAI's Sora announced in February 2024.
US and Chinese officials hold first bilateral talks on AI safety and risks in Geneva.


The Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) and three other agencies require companies to file algorithms for review, reflecting concerns over how they spread online content and make decisions.
The US puts export controls on semiconductors and key hardware that Chinese firms need to train AI, severely limiting their access to leading-edge graphic-processing units (GPUs).
Baidu announced ERNIE Bot, a conversational AI bot built on the company's LLM ERNIE. It is widely seen as a response to US-based Open AI’s ChatGPT of November 2022.
The CAC releases draft rules on generative AI, building on existing synthetic content rules and reflecting the CAC’s focus on controlling online content.
China becomes the first country to regulate generative AI with final rules. Public chatbots and the underlying models must pass a review – a de-facto licensing regime.
The CAC greenlights ERNIE Bot and 10 other models for release. The approvals signal regulators' balancing act between security and development and shows censorship is not an insurmountable obstacle.
China signs the Bletchley Declaration, the outcome of a major AI safety summit hosted by the UK. China's involvement with the US and other democratic nations shows shared concern around risks of AI.
Top Chinese and Western scientists meet in Beijing to discuss safety and existential risks associated with advanced AI systems.
The Government Work Report to the National People's Congress proposes the "AI+" initiative to deepen integration between AI and the real economy.
OpenAI blocks API access for China-based developers after shutting down online influence and hacking networks linked to China and others, further decoupling US and Chinese generative AI ecosystems.
A team at Tsinghua University's Department of Precision Instruments develops Tianmoc, a brain-inspired chip designed for AI applications.
Tech progress
- DeepSeek’s announcement of its forthcoming V3.1 model emphasized changes to increase compatibility with domestically produced AI accelerator chips. Its support for a new data format called “UE8M0 FP8” is aimed at better conforming to domestic chips for better performance. The move may increase demand for domestic chips. (Source (CN): Caijing, August 23, 2025)
- At the World Artificial Intelligence Conference in Shanghai, Alibaba presented three new open-source large language models from its Qwen series. It also celebrated Qwen’s status as the largest open-source model family in China (and by some metrics the world). (Source (CN): Leiphone, July 27, 2025)
- China’s first World Humanoid Robot Games were held in August, alongside the 10th World Robot Conference in Beijing. With 280 teams from 16 countries, robots competed in sports such as sprinting, football, and kickboxing. The event reflected China’s efforts in developing humanoid robot technologies with leading companies such as Unitree. (Source (CN): State Council Information Office, August 15, 2025)
Domestic dynamics
- China published new implementation guidelines of its “AI+” action plan, a nationwide strategy to enhance AI integration in different fields ranging from economic sectors to public infrastructure. It sets milestones for the country to move into an “intelligent economy” and “intelligent society” by 2035. (Source (CN): gov.cn, August 21, 2025)
Foreign involvement
- At its World Artificial Intelligence Conference in Shanghai, China released an Action Plan for Global AI Governance, which builds on an initiative from 2023 and invites collaboration to countries around the world. It also proposed creating a global AI cooperation organization. (Sources (CN, EN): gov.cn, July 26, 2025, english.gov.cn, July 26, 2025)
Artificial Intelligence in China: Profiling the actors
Publications




